RaspberryPi

|
Diseños
Todos los diseños disponibles se encuentran en el siguiente enlace.
Sistemas Operativos
Proyectos interesantes
- 6 proyectos para hacer con la RaspberryPi
- 10 proyectos para hacer con la RaspberryPi
- 10 mejores proyectos
- Página de proyectos para RaspberryPi
- Controlando la RaspberryPi con un Smartphone
- RaspberryPi con Android
Configuración puerto GPIO
Guías de instalación
OpenCV
Las librerías de openCV se instalan mediante un script autoejecutable.
$ wget https://raw.github.com/jayrambhia/Install-OpenCV/master/Ubuntu/2.4/opencv2_4_5.sh $ chmod +x opencv2_4_5.sh $ ./opencv2_4_5.sh
Posibles problemas
No se pudieron obtener algunos archivos, ¿Quizá deba ejecutar <<apt-get update>> o deba intentarlo de nuevo con --fix-missing?
Para resolver, dejar instalar y cuando acabe, hacer:
$ sudo apt-get update
Y volver a ejecutar
$./opencv2_4_5.sh
Una vez compilado despues de unas cuatro horas y media:
$ cd programs/OpenCv/opencv-2.4.5/build $ sudo make install
A partir de aquí es necesario seguir el tutorial del la siguiente página.
El paso 2 trata sobre instalar userland que es un programa llamado rapistill que usa el acceso a la cámara de la raspberry y demás.
El paso 3 es para crear el primer programa y poner a prueba los pasos anteriores.
Problema
A la hora de compilar con make (una vez modificado el CMakeLists.txt)
fatal error EGL/egl.h: no such file or directory
Se soluciona instalando las librerías legl de synaptic que son las genéricas. Se han instalado las siguientes:
eglibc-source libegl-0.2-0 libegl-dev
Se instalarán algunas dependencias más pero con estas valen. El último paso es modificar el CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(camcv) SET(COMPILE_DEFINITIONS -Werror) include_directories(/opt/vc/host_applications/linux/libs/bcm_host/include) include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/vcos) include_directories(/opt/vc/) include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/vcos/pthreads) include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/vmcs_host/linux) include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/khronos/include) include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/khronos/common) add_executable(camcv RaspiCamControl.c RaspiCLI.c RaspiPreview.c camcv.c RaspiTex.c RaspiTexUtil.c teapot.c models.c square.c mirror.c) target_link_libraries(camcv /opt/vc/lib/libmmal_core.so /opt/vc/lib/libmmal_util.so /opt/vc/lib/libmmal_vc_client.so /opt/vc/lib/libvcos.so /opt/vc/lib/libbcm_host.so /opt/vc/lib/libGLESv2.so /opt/vc/lib/libEGL.so)
Ahora sí se puede compilar con make y no da problemas.
Finalmente para añadir opencv al programa seguir el paso 4 del tutorial
Para esta parte es necesario haber instalado el lilbfacerec (reconocimiento facial)
projects $ git clone https://github.com/bytefish/libfacerec.git $ cd libfacerec $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make
Ya se puede modificar el CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(camcv)
SET(COMPILE_DEFINITIONS -Werror)
#OPENCV
find_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )
link_directories( /home/pi/projects/libfacerec )
include_directories(/opt/vc/host_applications/linux/libs/bcm_host/include)
include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/vcos)
include_directories(/opt/vc)
include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/vcos/pthreads)
include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/vmcs_host/linux)
include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/khronos/include)
include_directories(/opt/vc/interface/khronos/common)
add_executable(camcv RaspiCamControl.c RaspiCLI.c RaspiPreview.c camcv.c RaspiTex.c RaspiTexUtil.c teapot.c models.c square.c mirror.c)
target_link_libraries(camcv /opt/vc/lib/libmmal_core.so /opt/vc/lib/libmmal_util.so /opt/vc/lib/libmmal_vc_client.so /opt/vc/lib/libvcos.so /opt/vc/lib/libbcm_host.so /opt/vc/lib/libGLESv2.so /opt/vc/lib/libEGL.so /home/pi/projects/libfacerec/build/libopencv_facerec.a ${OpenCV_LIBS})
En el archivo camcv.c a partir de la línea 232 está el código preparado para procesar la imagen con OpenCV.
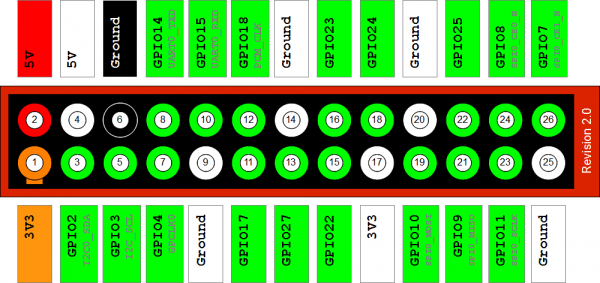
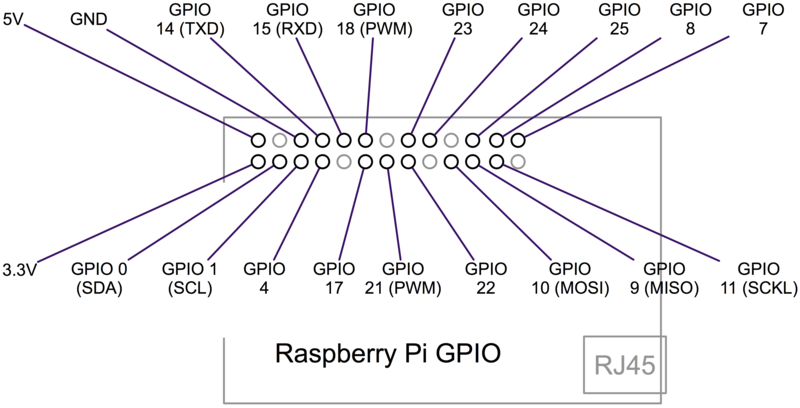
GPIO
El puerto GPIO tiene las siguientes características:
The GPIO connector actually has a number of different types of connection on them. There are:
- True GPIO (General Purpose Input Output) pins that you can use to turn LEDs on and off etc. - I2C interface pins that allow you to connect hardware modules with just two control pins - SPI interface with SPI devices, a similar concept to I2C but a different standard - Serial Rx and Tx pins for communication with serial peripherals
In addition, some of the pins can be used for PWM (pulse Width Modulation) for power control and another type of pulse generation for controlling servo motors called PPM (Pulse Position Modulation). In this tutorial, you are not actually build anything, but you will learn how to configure your Raspberry Pi and install useful libraries ready to start attaching some external electronics to it.
En la página aparece un overview y los primeros pasos para configurar el puerto.
Primeros Pasos
$ sudo apt-get install git
$ git clone http://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-Raspberry-Pi-Python-Code.git
$ cd Adafruit-Raspberry-Pi-Python-Code
Es un repositorio de proyectos-ejempos en Python para gobernar el puerto GPIO. Para poder usarlos es necesario tener las librerías instaladas
Librerias Python
GPIO
En el siguiente link están los pasos a seguir. Se reducen a instalar las librerías de GPIO para la Raspberry:
$sudo apt-get update
$sudo apt-get install python-dev
$sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpio
Para ejemplos visitar esta página
- Ejemplo
#!/usr/bin/python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
channel = 15
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(channel, GPIO.OUT)
for i in range (10):
GPIO.output(channel, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(3)
GPIO.output(channel, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(3)
GPIO.cleanup(channel)
PWM:
#!/usr/bin/python
fimport RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT)
p = GPIO.PWM(12, 0.5)
p.start(1)
input('Press return to stop:') # use raw_input for Python 2
p.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
picamera
En este link están los primeros pasos y toda la documentación de la librería picamera en python.
OpenCv Python
Leer estos tutoriales de opencv en python.
I2C
En esta página se recogen los pasos para la correcta configuración.
![]() Este obra está bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-CompartirIgual 3.0 Unported.
Este obra está bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-CompartirIgual 3.0 Unported.